

Inflammation of peripapillary retinal layers and the optic nerve can result in a macular star seen in neuroretinitis. Disc leakage on fluorescein angiography and a delayed response on visual-evoked potential testing can reveal the presence of optic neuropathy in leptospirosis. Involvement of the optic nerve can manifest through papillitis, optic neuritis, neuroretinitis, and optic disc hyperemia (found in 3%-64% of case presentations). Anterior uveitis is typically mild and self-limiting while panuveitis can be severe and relapsing.

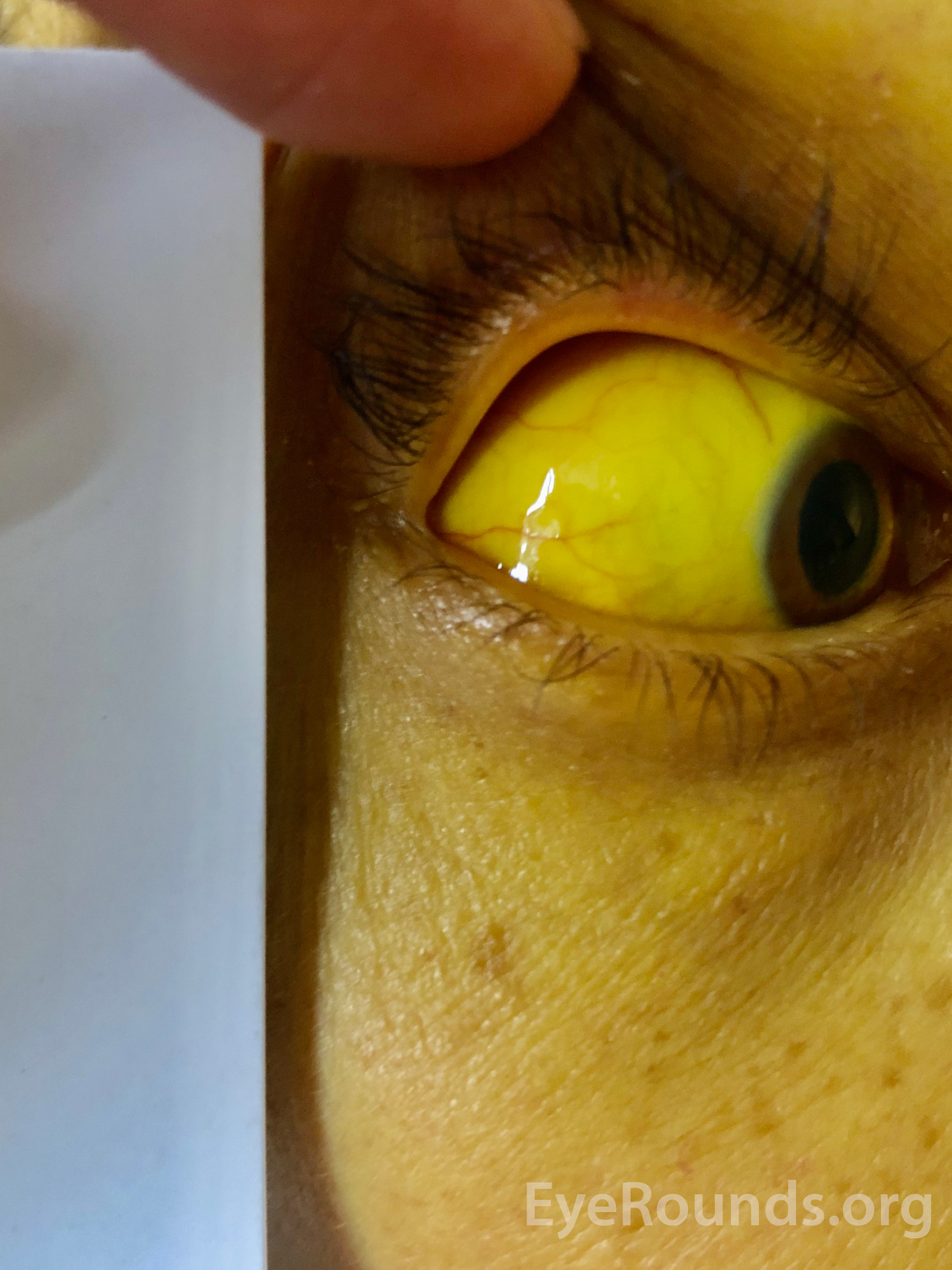
Unilateral or bilateral uveitis (anterior or diffuse and acute or recurrent) generally develops 6 months after a systemic infection, although presentation can range from 2 weeks to a few years, with clinical signs of iridocyclitis, iritis, hypopyon, vitreous inflammatory reaction, cataract, retinal vasculitis, and papillitis. Ophthalmic findings of the late immune phase (Weil disease) of infection include nongranulomatous uveitis, interstitial keratitis, conjunctival suffusion, cranial nerve palsies (third, fourth, sixth, or seventh cranial nerves) retinal vasculitis and hemorrhages, and optic neuropathy. Ocular findings in the leptospiremic acute phase of the illness include sub-conjunctival hemorrhage, scleral icterus, circum-corneal congestion without conjunctival discharge, conjunctival suffusion, and chemosis. Since there is no widely available human vaccine, preventative measures include avoiding potential sources of infection (contaminated water or food), antimicrobial prophylaxis (doxycycline) in individuals at high risk of exposure, and vaccination of animals. Specifically, the presence of serovar-specific lipopolysaccharide (LPS) with an increase of Interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p70, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokines and selective neutrophil infiltration in aqueous humor is indicative of endotoxin as a possible causative factor for leptospiral uveitis. The etiology of ocular features of leptospirosis has been postulated as a host immune response and/or toxin production. In addition, leptospiral uveitis is most prevalent in young to middle-aged men, likely from their higher involvement in agricultural work.
The incidence of infection is 10 times higher in tropical and subtropical climates as opposed to temporal climates. Leptospirosis is the most common zoonotic illness globally with an estimated 500,000 high-risk cases per year and 30% mortality rate.

cattle, pigs, horses, racoons, porcupines, domesticated dogs) or their body fluids (especially urine) via water or soil contamination. The primary mode of human transmission is direct or indirect contact with infected animals (e.g. Both anterior and posterior segment ophthalmic manifestations can occur in Leptospirosis and this Eyewiki emphasizes these ocular findings. Weil disease is the late icteric phase following severe systemic manifestations including interstitial nephritis, uremia, oliguria, kidney lesions, vascular injury, meningitis, jaundice, psychosis, confusion, and delirium. The majority of cases present with the acute (anicteric) phase consisting of self-limiting clinical manifestations including sudden fever, myalgia, headache, scleral icterus, chemosis, nausea, anorexia, and abdominal pain. This tropical disease is the most common zoonotic illness worldwide. Leptospirosis (Weil disease) is a gram-negative, water-borne, spirochete that is part of the Leptospira genus within the Leptospiraceae family.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
